Butane and propane are two light hydrocarbons that are used either separately or together to create high-terpene, high-cannabinoid extracts with minimal post-processing required.
The main difference between butane and propane is that butane has a longer carbon chain and removes more constituents due to its polarity. It also generally creates harder, darker-colored extracts that are slightly lower in terpenes while propane creates softer, lighter-colored extracts that are especially high in terpenes. Typically, operators use a single solvent to maintain consistency for production purposes.
Main Considerations in Butane vs. Propane Extraction
Boiling Point
Propane’s boiling point—-43.6°F (-42°C)—is much lower than butane’s boiling point of 31.1°F (-0.5°C), Which means, higher Vapor pressure is common with Propane due to the volatility at (varying) stored temperatures. The upside to this, however, is that propane is easier to separate from the final product than butane, which has the slowest recovery time. Both hydrocarbons can be boiled off the crude extract while leaving temperature-sensitive terpenes intact.
Terpene Extraction
Propane extraction strips more terpenes from the starting material—sometimes to the extent that the resulting extract is harsher on the throat. That’s one of the reasons why butane and propane are often combined: The propane component makes the terpene extraction more efficient while the butane component keeps the level of terpenes low enough to ensure the smoothest possible smoke.
Color and Viscosity
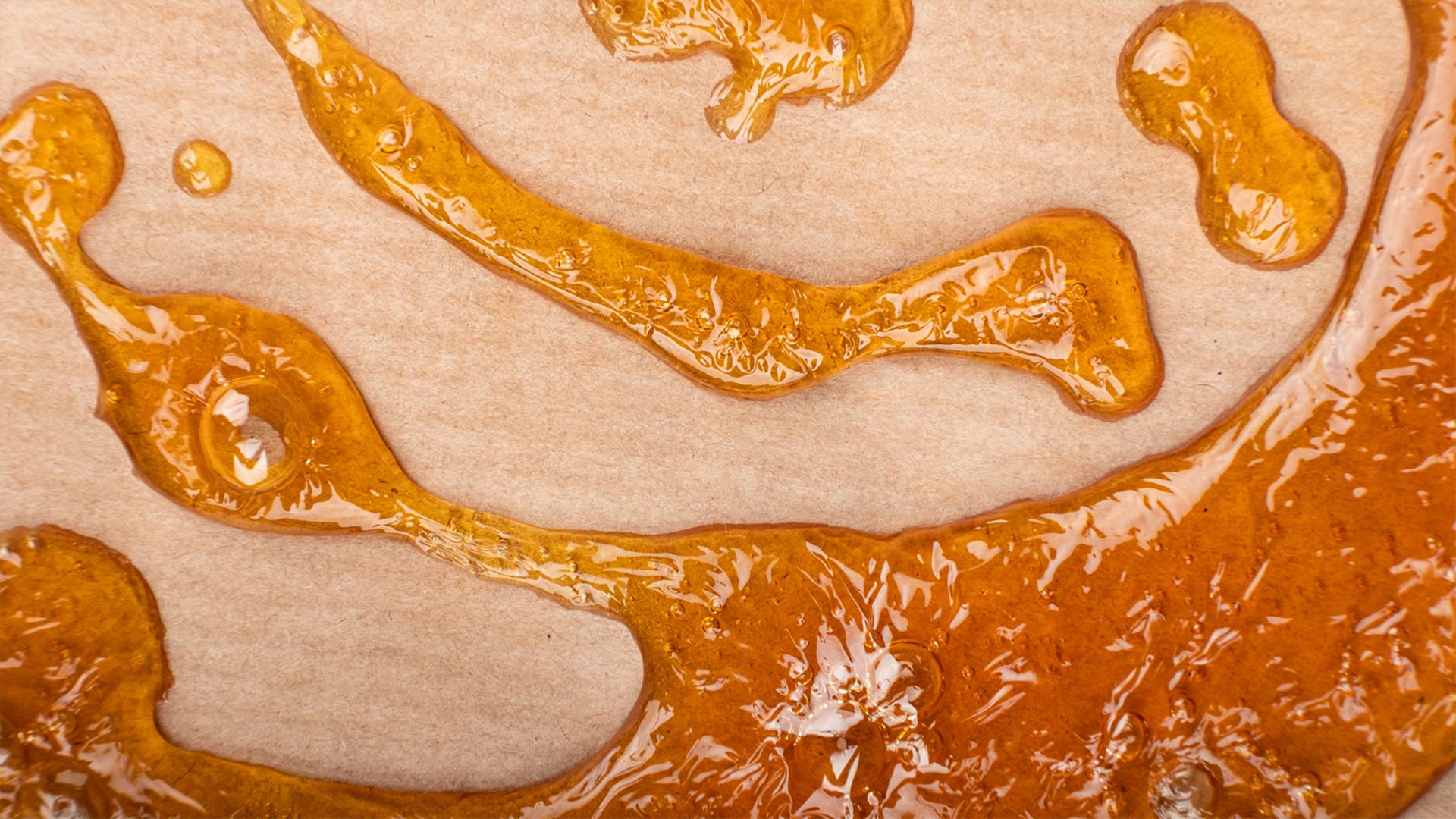
Propane hash oil (PHO) is a lighter color than butane hash oil (BHO) and has a lower viscosity. The propane extraction process results in an extract that’s either sticky or has a sugar-like consistency, whereas butane extraction can be used to make dark, solid extracts (like shatter) or golden-colored thick extracts (like badder and budder).
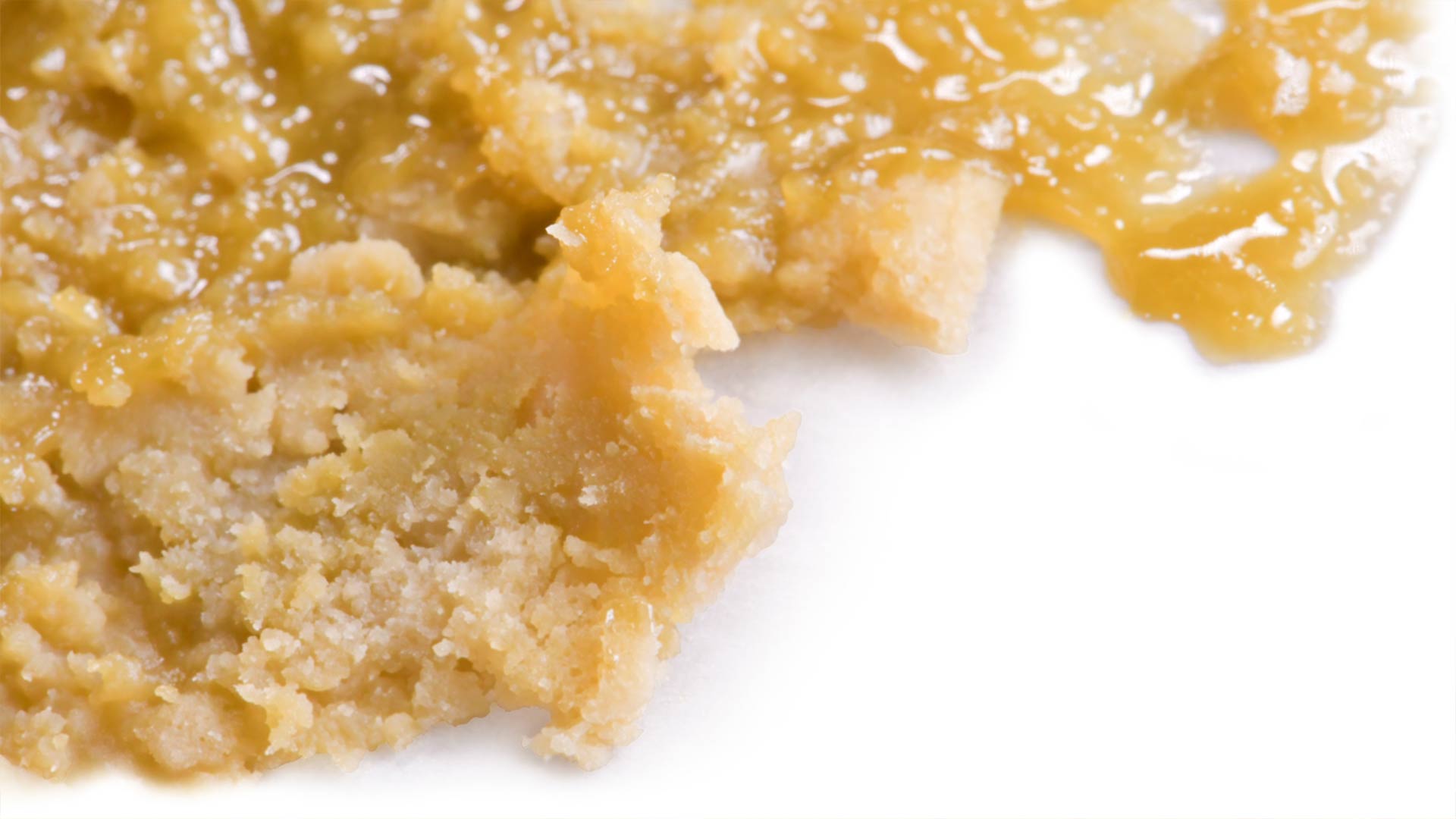

Blending Solvents
A 70% butane/30% propane blend is often used because Propane accelerates the Butane through the CLS without the need of Nitrogen. For budder and shatter extracts 100% propane can work well for sugar consistencies and high-terpene extracts. When blending solvents, remember:
- The temperature must be cold enough for the solvent with a lower boiling point.
- The pressure must be high enough for the solvent with higher vapor pressure.
- Temperature can be used to separate the residual solvents separately when purging the crude extract in a vacuum oven.
Because solvent extraction is a batch process, it’s common for extraction artists to experiment with blends, temperatures, and pressure to make the highest quality of concentrate possible with their particular extraction equipment.
The Solvent Extraction Process
Step 1: Soaking
In the first step, ground cannabis plant material is soaked in butane, propane, or a mixture of both to separate the active compounds from the plant material. This typically happens in a tank inside of a closed-loop extraction system. The solvent is cycled through the system and collects the active compounds as it passes over the cannabis material.
Step 2: Separation
The solvent is separated from the active compounds in a vacuum oven and recaptured through a recovery process for reuse.
Step 3: Further Refinement
After solvent extraction, the extract is typically winterized to remove fats, lipids, and waxes. Further refinement can then be performed to produce vape oils or distillate. Otherwise, the extract is ready for sale.
Step 4: Extraction Solvent Storage
After separation and capture, the residual butane and propane solvents are typically refined and stored in their liquid state, which means keeping them at the right temperature and pressure until the time comes to use them again.
Tips for Solvent Extraction:
Cold Extraction vs. Room Temperature Extraction
Whether you’re using butane, propane, or a mixture of both, the extraction process can be completed at room temperature or low temperature.
Room-Temperature Extraction
The advantages of room-temperature extraction are that it’s more efficient and results in a higher yield. The disadvantage is that more fats and waxes are extracted along with the cannabinoids and terpenes and the crude extract must be winterized before it can be offered for sale.
Low-Temperature Extraction
Compared to room-temperature extraction, low-temperature extraction is less efficient and produces a lower yield. However, there are often few or no fats and waxes and the extract may not require winterization.
Keep in mind that butane has a higher boiling point than propane, so room-temperature extraction is more practical for butane vs. propane extraction.
Importance of a Pure Solvent
Butane has received a “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) rating by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, butane fuel contains methyl mercaptan to give it an odor that can help to detect leaks, so you should only use pure and uncontaminated instrument-grade butane or n-butane (which is at least 99.5% pure) for cannabis extraction.
When purchasing butane or propane, ask for a certificate of analysis (COA) that shows the parts per million (ppm) of the constituents in the solvent blend. Distilling butane and propane before use and after recovery is also a good precaution to take. Closed-loop extraction equipment can (and should) include a refinement step before hydrocarbons are stored for reuse.
Safety Measures
Butane and propane are flammable solvents that can be extremely dangerous if proper care isn’t taken during cannabis extraction. In the United States, hydrocarbon extraction laboratories need to comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) requirements and use closed-loop extraction equipment as well as ensure the required permits, licenses, and inspections.
At a minimum, the processor will need to think about:
- Gas detection systems and alarms
- Adequate ventilation
- Training for extraction technicians
- Electricity-free recovery pump to eliminate a major ignition source
- The ability to suppress fire in the case of catastrophic equipment failure
Other Extraction Methods
Hydrocarbon extraction is one of the most popular extraction methods today thanks to its cost-effectiveness, its efficiency, and the high terpene content of the extracts. However, other extraction methods are also emerging that provide an alternative for budding concentrate entrepreneurs.
Solventless Rosin Press Extraction
A rosin press uses heat and pressure to squeeze the cannabinoids and terpenes out of flower trichomes rather than drawing them out with a solvent. Different rosin press temperatures and pressures can be used to create different concentrate textures and a higher or lower percentage of terpenes.
If you’d like to try your hand at creating rosin, a manual rosin press is a lightweight and most cost-effective machine to start with. As you scale, a pneumatic rosin press can handle industrial amounts of plant material.
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction is similar to hydrocarbon extraction—a gas is forced into its liquid form for the purposes of cannabis extraction—except that any supercritical fluid that remains after CO2 extraction simply bubbles off the extract at the end, so there’s no chance of any leftover solvent remaining in the final product.
On the flip side, supercritical carbon dioxide extraction doesn’t usually extract as many terpenes as hydrocarbon extraction, so it’s more commonly used for creating THC and CBD distillates.
Butane vs. Propane Extraction Is Just the Beginning
Propane and butane extraction equipment allows processors to create connoisseur-grade concentrates in a very cost-effective way—especially when the best solvent blends are used for each kind of final product.
If you would like to try your hand at this extraction method—whether 100% butane, 100% propane, or a blend of both, be sure to use a laboratory that’s licensed for hydrocarbon extraction and uses closed-loop extraction equipment that ensures maximum solvent recovery. Once you’re set up, you can experiment with the best blends of butane and propane and create some incredible extracts.













